In today’s healthcare landscape, Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is the backbone of a practice’s financial health. From a patient’s first appointment to the final payment, each step of RCM plays a key role in a practice’s cash flow, efficiency, and overall success. In this article, Medlife will guide you through the ins and outs of RCM, showing how a well-managed revenue cycle can mean stronger cash flow, fewer denied claims, and an overall better experience for both staff and patients.
What Exactly is Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)?
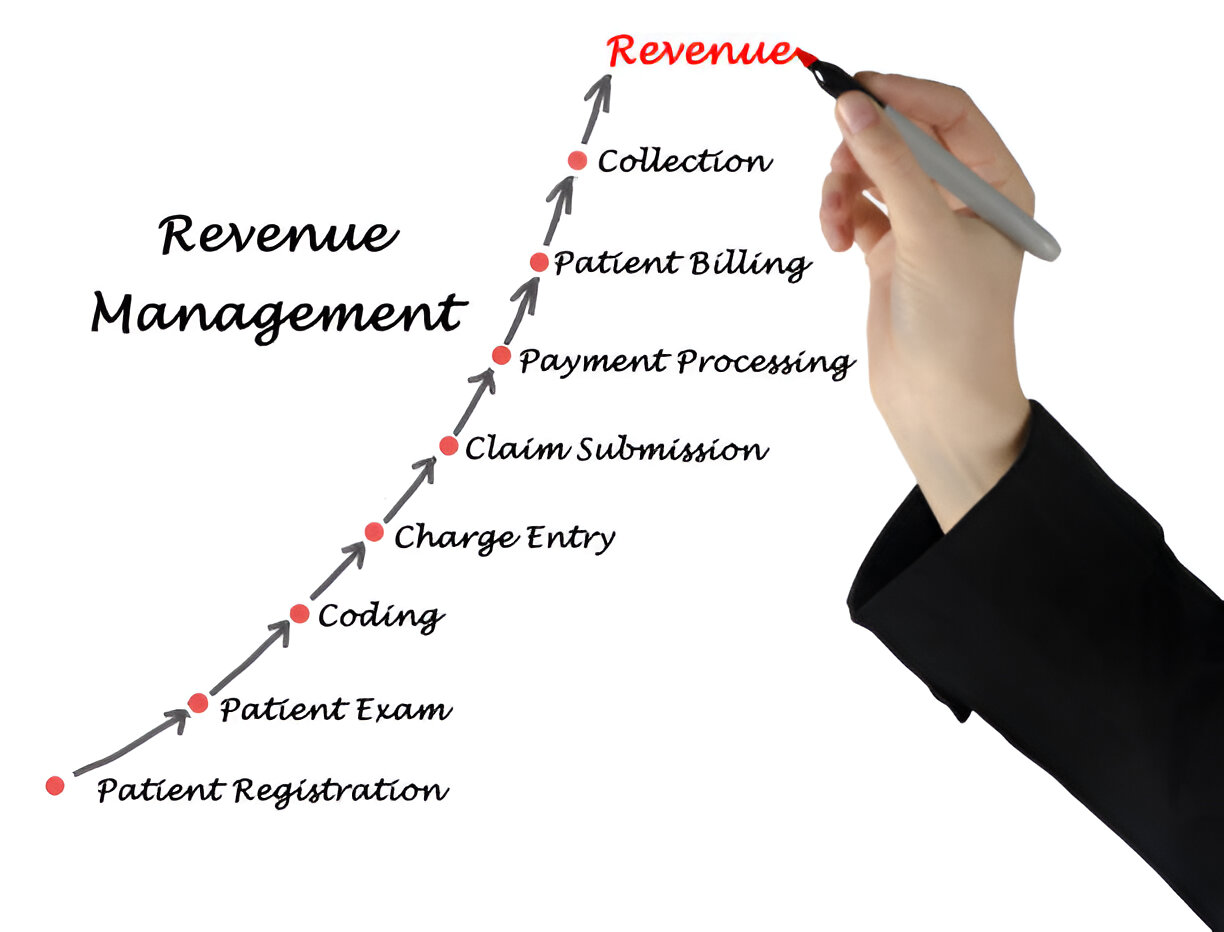
Think of Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) as the roadmap for tracking and managing patient payments from start to finish. RCM starts the moment a patient schedules an appointment and continues through registration, claims submission, denial management, and payment. Each step requires careful attention to avoid delays and lost revenue. In short, an efficient RCM process supports the practice financially while also streamlining the experience for patients.
Breaking Down the Phases of RCM
A well-rounded RCM process involves several key phases, each essential to a practice’s financial success. Here’s a closer look at each step:
- Patient Scheduling and Registration
The revenue cycle starts when a patient schedules an appointment. Collecting accurate information, including insurance details, at this stage is crucial. The more complete the data, the fewer obstacles there will be down the line in submitting claims and collecting payments. - Insurance Verification and Authorization
Verifying insurance coverage and obtaining necessary pre-authorizations is essential to avoiding unexpected denials. Confirming a patient’s insurance benefits early in the process sets clear expectations for both the patient and the practice, helping prevent surprises. - Charge Capture and Coding
Once the patient has received services, it’s time to capture the charges and code them accurately. Medical coding directly affects reimbursement, so accuracy is crucial to ensure that the practice gets paid fully and promptly. - Claims Submission
Submitting the claim to the payer is a step that requires attention to detail. Reviewing claims for accuracy and compliance with payer guidelines helps reduce the risk of denials and speeds up the payment process. - Denial Management and Appeals
Even with best practices in place, some claims will inevitably be denied. Denial management involves analyzing the reasons for these denials and following up with appeals if necessary. Efficient denial management helps recover revenue that would otherwise be lost and improves the overall claim approval rate. - Payment Posting and Collection
Once payments start coming in, posting them accurately is key. Tracking payments from both payers and patients allows the practice to stay on top of any outstanding balances and follow up when needed, keeping cash flow steady. - Reporting and Analysis
Regularly reviewing RCM data allows practices to spot trends, evaluate performance, and make improvements. Data insights can help practices identify areas where they might improve processes, which can mean faster payments and fewer issues.
Why Revenue Cycle Management is Crucial for Healthcare Practices
RCM isn’t just about payments; it’s the financial foundation of a healthcare practice. When RCM is done well, it can:
- Improve Cash Flow: Fewer delays in payments mean smoother cash flow.
- Reduce Errors: Accurate data entry and careful review minimize claim rejections.
- Enhance Patient Satisfaction: A streamlined billing process leads to fewer billing issues, making the patient experience smoother.
- Support Smart Decision-Making: Reporting and data analysis provide the insights needed to make informed financial decisions.
A well-managed revenue cycle ensures that practices can focus on what they do best—providing quality care to patients—without the financial hiccups.
Challenges in Revenue Cycle Management
Despite its importance, RCM can come with its own set of challenges:
- Data Entry Errors
Mistakes in patient information or coding can lead to denied claims or delayed payments. Taking the time to gather accurate information at the start makes a big difference in avoiding these issues. - Complex Billing Regulations
Navigating insurance regulations and payer guidelines can be complicated. Staying compliant with these rules is essential to avoid penalties and prevent delays. - Limited Resources
Smaller practices may not have the staff to dedicate solely to RCM, which can lead to gaps in the revenue cycle. Many practices choose to outsource RCM, allowing them to benefit from specialized expertise without the expense of a full-time team.
The Role of Technology in Transforming RCM
Modern technology is reshaping RCM, helping practices reduce errors and streamline processes. Some key ways technology enhances RCM include:
- Automated Billing and Coding: Automation minimizes human error and speeds up the billing and coding process.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Analytics tools help practices identify trends and make informed decisions, improving efficiency.
- Electronic Claims Submission: Submitting claims electronically reduces processing time and helps avoid rejections by ensuring claims are correctly formatted from the start.
Embracing technology not only reduces the administrative burden on staff but also improves revenue recovery and operational efficiency.
How Medlife Supports Effective Revenue Cycle Management
At Medlife, we understand that RCM can be complex and time-consuming. Our RCM services are tailored to streamline each stage, helping healthcare providers reduce denials, boost cash flow, and focus on patient care. Here’s how we support practices:
- Ensuring Compliance with Payer Regulations: We stay on top of evolving payer rules to help practices remain compliant and avoid unnecessary rejections.
- Minimizing Delays in Claims Processing and Payment Posting: Our team’s precision and experience help practices avoid delays, keeping cash flow consistent.
- Providing Detailed Reporting for Financial Insights: Our data-driven approach gives practices the information they need to make informed decisions and optimize their revenue cycle.
With Medlife’s expertise, healthcare practices can navigate the complexities of medical billing with confidence, knowing their revenue cycle is in capable hands.
Building a Stronger Practice with Efficient RCM
A well-managed revenue cycle is essential not only for a practice’s financial health but also for delivering a seamless patient experience. By focusing on accuracy, efficiency, and proactive management, practices can transform RCM into a tool for growth and stability. Medlife is here to support healthcare providers in achieving optimized RCM, with services that meet the unique needs of each practice. Partner with Medlife to make sure your RCM is as efficient and reliable as your patient care.